The Notecards
Combining prepaid cellular connectivity, low-power design, and secure "off-the-internet" communications in one System-on-Module.
Meet the Notecards

-
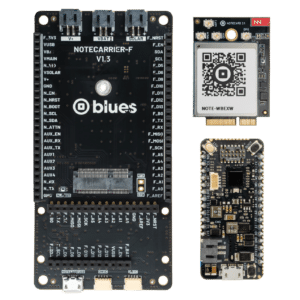
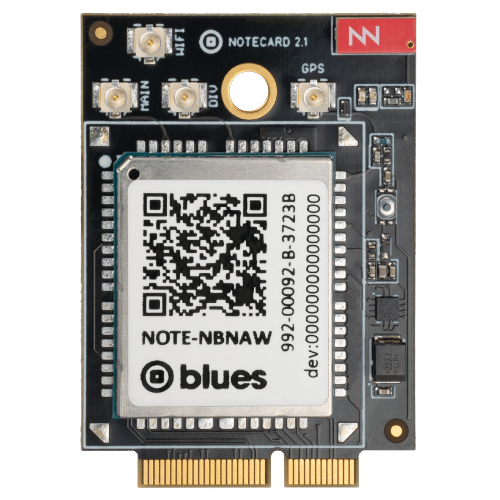
Notecard Cell+WiFi
- Global cellular coverage over LTE CAT-1, CAT-M, or NB-IoT
- Automatic failover between cellular and Wi-Fi in the event of a disruption
- Precise location tracking through a GNSS/GPS module or our Wi-Fi Triangulation feature
- Dual-embedded SIM option that expands your international coverage and provides better signal quality
- Onboard ultra-low-power ARM® Cortex®-M4 MCU with 2MB Flash
-
Notecard Cellular
- Global cellular coverage over LTE CAT-1, CAT-M, or NB-IoT
- Precise location tracking through a GNSS/GPS module
- Embedded SIM with pre-provisioned network access

-
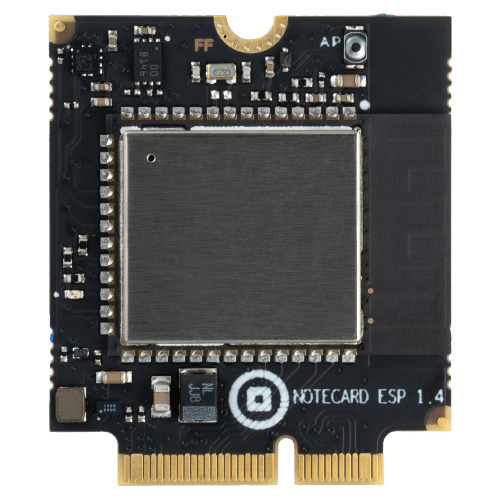
Notecard WiFi
- Compatible with Wi-Fi 802.11, 2.4Ghz b/g/n, and Notecard pinouts for additional functionality
- Wi-Fi Triangulation lets you determine a device’s location, even when indoors, with as little as a single network
- Ideal for line-powered device clusters with a high sampling rate, fixed-room scenarios, and cell signal-challenged locations

-
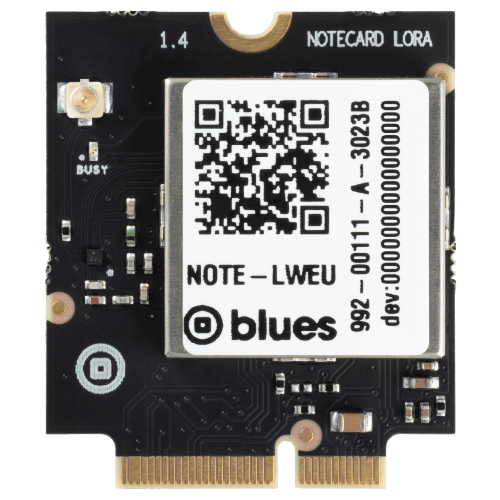
Notecard LoRa
- Compatible across all layers of the LoRa network, including LoRaWAN and The Things Network
- Ultra-low power design allows you to operate for years on a battery and even extend battery life with sleep mode, which can wake up on sensor events
- Capable of communicating over a mile in urban areas and up to 5 miles in rural areas
-
Starnote
- Streamlined Satellite Connectivity for Only $49
- Integrated Data Package
- Backup Connectivity
- Cost-Effective Hardware

-
Notecard XP
- Customizable selection of Notecard features
- Fast-track your time to market
- Move between any radio access technologies
- Effortless data routing to any cloud application
- Field-upgradeable
- Starting at just $19
-
Built with Wireless Harmonization
The Blues ecosystem is built around the concept of wireless harmonization that enables you to
create a solution for 1 connectivity technology and seamlessly apply that solution to multiple technologies with minimal design or software changes.This innovative approach ensures that no matter which Notecard you leverage, you’ll still experience
the same plug-and-play JSON interface, industry-leading security, easy provisioning at scale, and secure data routing with Notehub.The Notecard lets your team focus on building game-changing products, not establishing connectivity.

Prototype Your Solution with our Starter Kits
The Notecard brings your ideas to life by connecting everything from industrial equipment to remote patient monitoring devices to the cloud.
Blues Starter Kit
Kit Includes Notecard + WiFi, Notecarrier F, Swan 3.0, Molex flexible dual Wi-Fi and Cellular Antenna